David Foster Wallace hung himself on September 15, 2008. On that day, the author of novels like The Broom of the System, Infinite Jest and (the unfinished) The Pale King resolved to shuffle off this mortal coil at the business end of a home-made gibbet (see “Word of the Week“). Having been hailed for years as a “genius” by a vast array of pundits and critics, his beautiful wife gone for the day, Wallace quite apparently felt that life was no longer worth living.
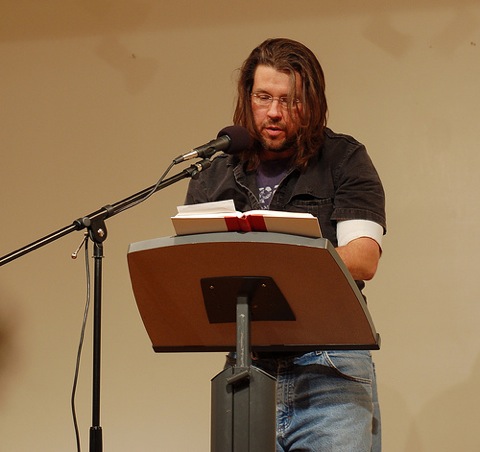

To all fans of Robert E. Howard, Wallace’s fate should evoke a certain amount of resonance. Wallace was in his forties (as opposed to REH’s 30.5 years of age) when he did himself in. Still, I’m sure DFW’s fans have been asking themselves that eternal question: “Why”? Wallace seems to have suffered from long-term depression. He even tried electro-convulsive therapy to alleviate his anguish, all to no avail. Anti-depressants were a mainstay of his existence, but Wallace felt that the drugs were creating a wall betwixt himself and the world he wanted to write about. According to D.T. Max of The New Yorker, in his article about DFW, “The Unfinished,” Wallace wanted, “to author things that both restructure worlds and make living people feel stuff,” (DFW’s quote to an editor). Is such a sentiment that far from what REH aspired to? In regards to his poetry and prose, Howard often expressed the view that he wasn’t measuring up to the standards he set for himself. In Wallace, we see a man who, despite all modern pharmacology and the welcoming embrace of post-modern criticism, just couldn’t carry on. Yet, there are those who feel that Robert E. Howard simply did not have sufficient reason to end his life. Fair enough. However, are those same post–mortem/post-modern critics (and their ilk) going to hold DWF to the same stringent standards of authorial behavior as they do REH, or does Wallace get a free pass because he wrote about the “real world” (as if Howard didn’t )?
Tom Shippey once stated that the three landmark works of the twentieth century (1984, The Lord of the Flies and The Lord of the Rings) were all works of “fantasy.” Personally, I’d also nominate several works of Robert E. Howard into that category (damn good company, in my opinion). Just as in the works cited by Shippey, the narrative is heightened to illuminate universal questions and truths. Wallace, also, did not shy away from going beyond the fields we know, at least in a temporal sense. His Infinite Jest is set in a post-post-modern future. When all’s said and done, how different is Wallace’s tale from that of Robert W. Chambers’ “The Repairer of Reputations,” wherein Castaigne is an uncrowned “King of the United States of America” and there is always a “Government Lethal Chamber” within easy walking distance? Wallace seems to have shared the depressed, nihilistic world-view engendered by RWC’s fictional play, The King in Yellow.
Shippey noted that “realism” in fiction often doesn’t seem capable of expressing the truths that many of us suspect lie beneath the facade of modern life. A cosmic, Lovecraftian view, in some respects. David Foster Wallace, in his non-fiction work, Everything and More, looked at the cosmic and infinite as well. Did the cosmic vistas that Wallace glimpsed affect his viewpoint? Did the “black seas of infinity” and “mad immensities of Night” darken his outlook? None can say now. All that can be said is that Robert E. Howard, enduring a hard-scrabble existence in central Texas during the Great Depression, had just as much, or just as little reason to live as Wallace did in twenty-first century California.
At a memorial service for Wallace, Jonathan Franzen had this to say: “People who believe that David’s death is the story of a biochemical imbalance don’t need the kinds of stories that David told.”
Replace “David” with “Robert E. Howard” and I think y’all might see why I wrote this blog.